Program Overview
The mission of the University of Osaka is to nurture outstanding individuals who possess a high sense of ethics and wish to become global citizens and leaders in a variety of fields worldwide under the objective of “Live Locally, Grow Globally”.
For this reason, the Department of Biological Sciences, the Department of Mathematics, the Department of Physics, and the Department of Chemistry in the School of Science have established the International Undergraduate Program in Science for international students.
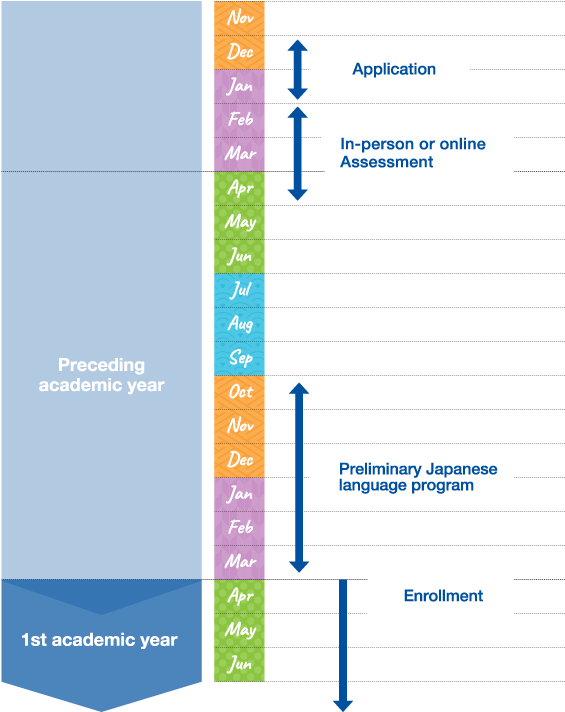
Students will be enrolled in the program for 4.5 years in total (half a year as a research student and 4 years as an undergraduate student) culminating in the award of a Bachelor’s degree.
This program is overseen by the International College and the School of Science, The University of Osaka.
Entrance examinations are conducted in English by each department (or in English and Japanese in the case of the Department of Biological Sciences and the Department of Mathematics). Note that basic proficiency in Japanese (at the level of JLPT N3, N2 in the case of the Department of Biological Sciences) is required at application time.
For six months prior to regular enrollment, students attend intensive Japanese language education classes and some preliminary science classes at the Center for Japanese Language and Culture (CJLC). During this time, students will be enrolled as research students. The nature of the Japanese language education classes will depend on each student’s individual Japanese language ability.
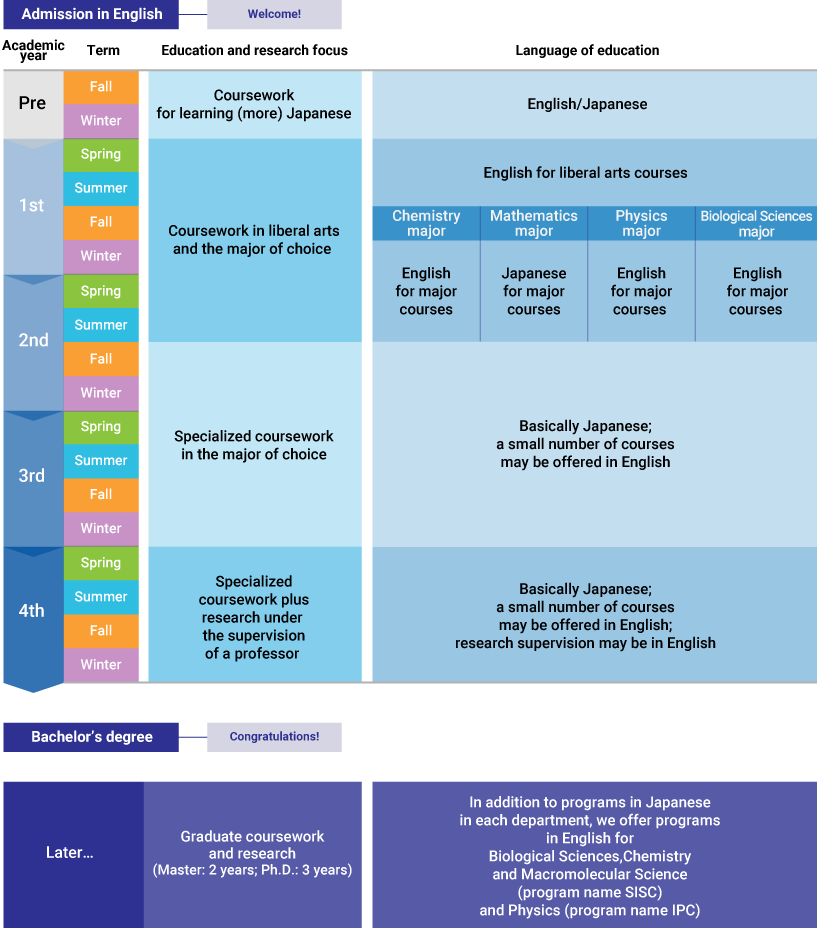
Students will then be enrolled as undergraduate students. In the first year, students will take classes mainly in English, and study liberal arts and science major subjects.
Further advanced Japanese language education will be offered until the end of the second year of the undergraduate program.
Students will focus on specific subjects in the students' respective majors from the second year, and the classes will transition from mainly being taught in English to mainly being taught in Japanese.
Students will be assigned to a specific laboratory to conduct research in their final year.
See the table below for more details.
Graduate School
After graduation, motivated students are welcome to proceed to graduate school in one of the six departments of our Graduate School of Science: Biological Sciences, Chemistry, Earth and Space Science, Macromolecular Science, Mathematics, Physics. See details on the webpage dedicated to graduate programs. In addition to programs in Japanese in each department, our Graduate School of Science offers degree (M.S. and Ph.D.) programs conducted in English for international students in Biological Sciences, Chemistry and Macromolecular Science (program name SISC) and Physics (program name IPC).
At our Graduate School of Science, research is active especially on the following topics.
- Department of Biological Sciences:
- biochemistry; biophysics; cell biology; comparative physiology; developmental biology; ecophysiology; epigenetics; evolutionary biology; genetics; genome informatics; molecular biology; molecular genetics; nanobiology; neurobiology; neuroethology; neurogenesis; oncogenesis; phylogenetic biology; plant ecophysiology; plant science; protein crystallography; structural biology; theoretical biology.
- Department of Chemistry; Department of Macromolecular Science:
- analytical chemistry; bio-nanotechnology; bioinorganic chemistry; biomolecular chemistry; bioorganic chemistry; biophysical chemistry; condensed matter physical chemistry; coordination chemistry; functional proteomics; informative polymer science; inorganic chemistry; macromolecular assemblies; macromolecular precise science; macromolecular structure, macromolecular structure, properties and functions; macromolecular synthesis and reactions; molecular beams; molecular biophysics; nanoporous materials; natural products chemistry; organic biochemistry; organic chemistry; organic fine chemicals; physical chemistry; physical organic chemistry; polymer assemblies; polymer functional chemistry; polymer physical chemistry; polymer reaction; polymer synthesis; polymeric materials design; protein crystallography; protein informatics; protein organic chemistry; protein physical chemistry; quantum chemistry; radiochemistry; radioisotopes; reaction dynamics; semiconductor materials; structural organic chemistry; structural thermodynamics; supramolecular chemistry; supramolecular crystallography; surface chemistry; synthetic organic chemistry; thermal and entropic science.
- Department of Mathematics:
- algebraic analysis; algebraic geometry; applied analysis; applied mathematics; combinatorics; commutative algebra; commutative ring theory; complex analysis; complex differential geometry; complex geometry; complex functions of several variables; complex manifolds; cryptography; differential geometry; dynamical systems; discrete geometry; discrete mathematics; discrete structures; discrete subgroups; fractals; information geometry; information theory; knot theory; mathematical engineering; mathematical physics; number theory; partial differential equations; probability theory; spectral theory; topology; transformation groups.
- Department of Physics; Department of Earth and Space Science:
- accelerator physics; astrophysics and cosmology; biophysics; condensed matter physics (theory and experiment); Earth and planetary material science; fundamental theoretical physics; geophysics; infrared and X-ray astronomy; intense laser science; interdisciplinary physics; mass spectrometry; non-equilibrium physics; nuclear physics (theory and experiment); particle physics (theory and experiment); physics of matter under extreme pressure and magnetic fields; planetary science; quantum physics; solid-state spectroscopy.